Understand the Terms¶
While saving in Bitcoin involves new concepts that don't otherwise exist in traditional economic models (such as a cryptographic ledger or UTXO sets), Bitcoin commerce is well aligned with traditional economics. The goal is simply to make and receive payments. For businesses it means selling goods and services -- getting paid in Bitcoin. For customers it means paying for goods and services -- as easily as you would pay in cash.
If you're coming from a fiat mindset, that is, commerce within fiat currency, Bitcoin commerce might seem odd at first, but you'll find it similar to traditional (pre-fiat) business models. This is because most of those traditional business models developed under a gold standard (a sound money standard).
As a result, you may find commerce under a Bitcoin standard to be intuitive and simple, almost naive, with none of the complex financialization one finds in modern fiat. There are however some new concepts, in particular new technical concepts that are worth understanding. We will describe and help demystify these new concepts, especially those necessary for understanding commerce in Bitcoin.
Lightning Network¶
Lightning is a Bitcoin payment network (proposed in this 2016 whitepaper). It allows virtually unlimited scaling of Bitcoin payments; and is built on top of the Bitcoin network as a second-layer network. In other words, the base-layer network has no visibility into lightning payments, but only provides final settlement of lightning channels.
In effect, Lightning is a network of channels between peer-to-peer Bitcoin nodes. Each channel provides liquidity between two nodes; a balance on each side. Lightning routes payments through the channels, allowing users anywhere in the network to send and receive Bitcoin anywhere else on the network (provided there is sufficient liquidity in the channels).
There are plenty of great resources to understand the implementation details of the Lightning Network, and while still very early it has seen widespread early adoption.
Public Channels¶
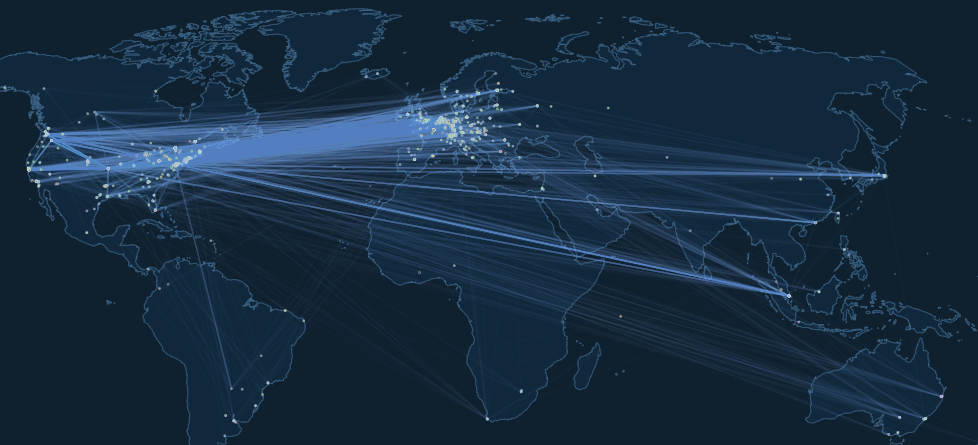
The above is a map of all public lightning channels. A public channel is simply a routable channel connected to the broader lightning network. This is a peer-to-peer network that routes payments anywhere. Another way to think about it, these are the channels that are not otherwise hidden. Public channels (and nodes) are discoverable on sites such as 1ml, amboss.space, or through LnRouter,
Importantly, anyone can use the Lightning Network, and anyone with a node (a Bitcoin full node with lightning software) can join. To join, simply request to open a channel with one of the nodes on the network. The moment you have at least one open channel, your node will be discoverable by others. Additionally, a well-connected node could potentially earn sats by routing payments.
Private Channels¶
A private channel is simply a channel between two nodes that is not otherwise discoverable. Private channels (and entire private networks) can easily be created for situations where all participants wish to remain private. For example, payments between nation states or business entities wishing to remain private.
Importantly, maintaining privacy requires an implicit trust amongst all participants in a private network. Should one of the nodes create a routable channel to the public Lightning Network, this would (depending on the software and configuration) make this formerly private network part of the public network.
work in progress
Invoices¶
...
LNURL¶
...
Lightning Address¶
...
Routing¶
...
Point of Sale¶
...